- Home
- Scarrows
- Mariners
- Cumberland
- Miscellaneous
Demerara
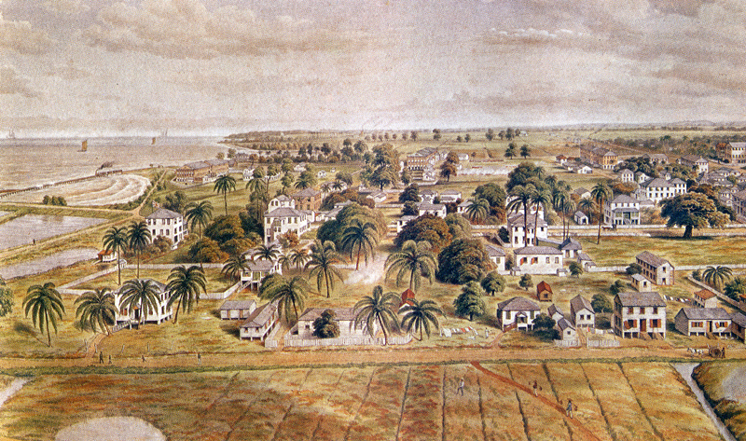
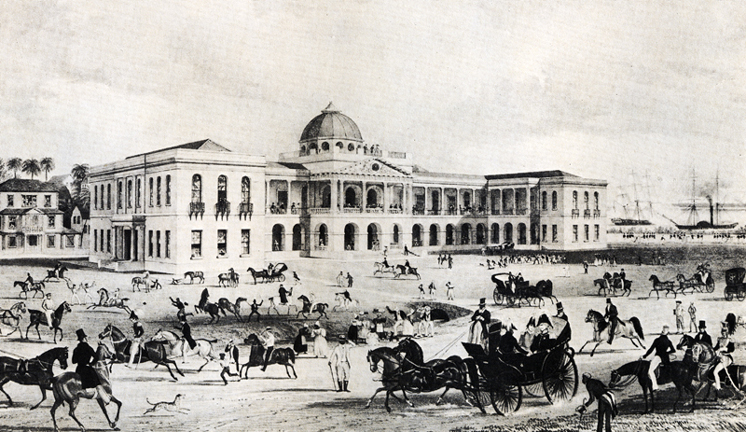
Georgetown Harbour, circa 1850
History
The Dutch established a settlement in Essequibo around 1616 at the mouth of the Mazaruni River where they built Fort Kyk-Over-Al (Kijk-Over-Al). In 1621, The merchants of Zeeland and other merchants united to form the West India Company and took over control of Essequibo. The Dutch established a second settlement, Berbice, east of Essequibo in 1627. The West India Company was reorganized and a new company, Nova Zeeland, emerged in 1657.
The cultivation of sugar cane began in 1658 along the Pomeroon River in Essequibo under the supervision of the Nova Zeeland Company and sugar was exported shortly thereafter. Sugar has been and continues to be one of the major exports of Guyana.
A third settlement, Demerara, situated between Essequibo and Berbice was established by the Dutch in 1741 and the three settlements were granted the status of Colony by 1773. The Dutch imported African slaves to work on their plantations during the early years of the colonies.
In 1763, Cuffy led a rebellion at Plantation Magalenenburg in the Colony of Berbice, beginning on February 23, against the harsh and inhumane treatment of slaves.
The British took control of the colonies, Essequibo, Berbice and Demerara, in 1781 and the military administrator, Lieutenant Colonel Robert Kingston, established Fort St. George as his headquarters in a part of the region presently known as Georgetown.
The British rule was short-lived and in 1782 the French and Dutch collaborated to sieze control of the colonies. The French demolished Fort St. George and built their own centre, called Longchamps (La Nouvelle Ville). The Dutch regained control of the colonies in 1784 and renamed the centre Stabroek.
The jurisdiction of the West India Company was transferred to the Estates' General in 1791 and in 1792 the United Colony of Demerara and Essequibo was established by the Dutch with the Colony of Berbice as a separate entity.

Georgetown
The British were once again in control of the colonies in 1796 and continued to hold them up to 1966, except for a brief interruption from 1802 to 1803. The Dutch were given control of the colonies in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens.
 The first constitution of the colonies, promulgated by the Dutch in 1792, was abolished by the British in 1812. During the same year, the centre Stabroek was renamed George Town in honour of the British Monarch, George IV. The British became the sole possessors of the United Colony and the Colony of Berbice in 1815 under the terms of the Treaty of Vienna.
The first constitution of the colonies, promulgated by the Dutch in 1792, was abolished by the British in 1812. During the same year, the centre Stabroek was renamed George Town in honour of the British Monarch, George IV. The British became the sole possessors of the United Colony and the Colony of Berbice in 1815 under the terms of the Treaty of Vienna.
On August 18, 1823, slaves on the East Coast of Demerara stopped working, siezed the arms of the Europeans and held them in captivity. The revolt began at Plantation Success and in the following two days spread up the East Coast to plantations as far east as Mahaica and between Success and Georgetown in the west.
The rebellion ended on August 20 following an engagement between British troops and the slaves during which an estimated 200 slaves were killed when the troops opened fire on them. The rebellion started because the slaves were of the impression that the Europeans were withholding their freedom which was granted to them by the King of England.
The United Colony (Essequibo and Demerara) and the Colony of Berbice became the Colony of British Guiana in 1831. The names, Essequibo, Demerara and Berbice, are still used today for the three Counties of Guyana. Sir Benjamin D'Urban, was appointed the first Governor of British Guiana. In 1834, Parliament Building also known as Public Buildings, home of the Republic's Parliament, was completed.

Slavery was abolished in British Guiana under the Emancipation Act in 1834 and replaced by a period of Appenticeship during which persons registered as slaves, six years old and upwards, were required to serve their former masters. Apprenticeship was abolished in 1838.
Following the abolishion of slavery, the British brought indentured labourers from Germany (1834), Portugal (May 3, 1835), India (May 5, 1838) and China (January 12, 1853) to work on the plantations.
During the early years of their freedom, the former African slaves purchased parcels of land and established villages in the coastal region, e.g., Buxton (1840) and Victoria (1839) on the East Coast of Demerara, and Queenstown (1838) on the Essequibo Coast.

A map of British Guiana showing its boundaries, prepared by the German Robert Hermann Schomburgk, was published in 1840 and this marked the beginning of the border dispute with Venezuela, which is still unresolved. An earlier map of British Guiana, compiled by Captain J.E. Alexander in 1832, did not show the boundary between the countries. In 1842, George Town became the city of Georgetown by "Royal" warrant.
The fires of April 3 and July 5, 1848 destroyed all of the wooden buildings on Water Street in Georgetown. The railroad extending from Georgetown to Plaisance, on the East Coast of Demerara, was opened in 1848. It was built by the Demerara Railway Company and was the first of its kind on the continent of South America. The East Coast Railway was later extended to Rosignal under a contract approved by the Government in 1890.
The Franchise Ordinance of 1849 rescinded the right to vote granted to women by Governor Carmichael in 1812. Gold was discovered on the bank of a tributary of the Cuyuni River in 1857 and the first Mining Regulations were passed in 1886. Diamond mining began later in the Upper Mazaruni at Putareng Creek. Gold production reached a record high of 138,528 ounces in 1893-94.
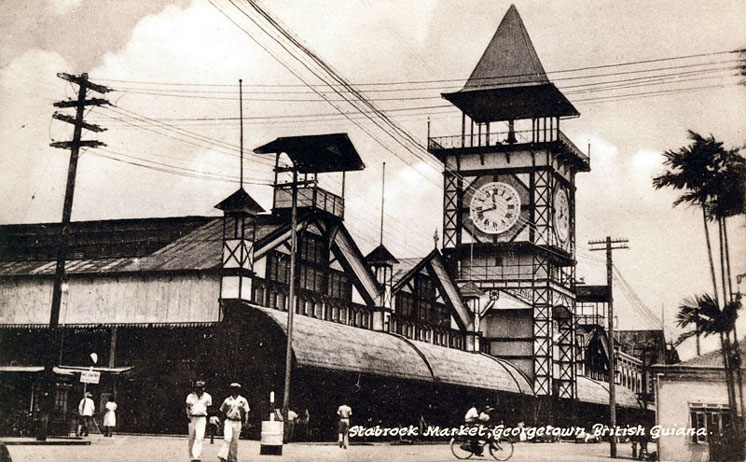
Construction of the sea wall was started following the flooding of the Kingston to Ogle area in 1853 and the first segment up to the Round House was completed in 1860. On April 24, 1870, Barrington Brown, a geologist, became the first European to see the Kaieteur Falls.
The falls has a 741-foot (226 m) single drop and is named after the Potamona Chief, Kaie, who according to Amerindian legend, paddled his canoe over the edge to appease his Gods. Brown and James Sawkins, also a geologist, were assigned to survey the Colony. They left the Colony in 1871 after completing surveys of the Corentyne, Berbice and Mazaruni rivers.
The British Guiana Constitution Ordinance of 1891 abolished the College of Electors and retained the structure of the Combined Court (Court of Policy and Financial Representatives) implemented by the Dutch in 1796. However, members of the Combined Court had to be elected from the constituencies and were required to have franchise income, whereas previously some of the members were nominated to the Combined Court.
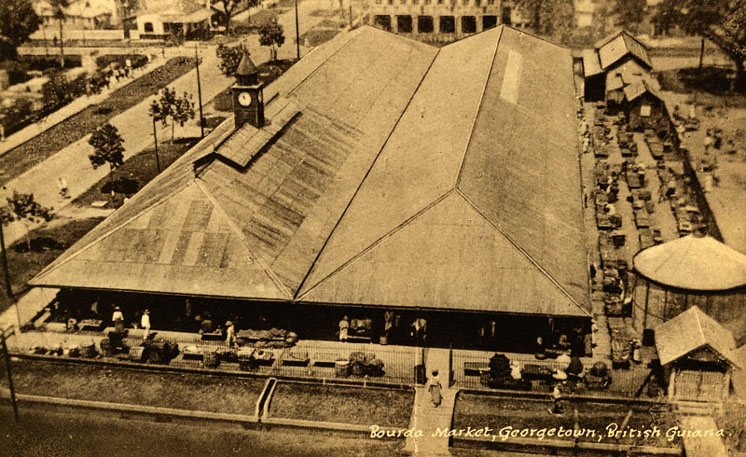
A competition for a Challenge Cup between cricket teams from Barbados, British Guiana and Trinidad was established during the later part of the 19th century. Cricket matches were played on the ground of the Georgetown Cricket Club (GCC), commonly known as Bourda, as early as 1883, between Trinidad and GCC, and later, in 1895 and 1897, between GCC and visiting teams from Britain. Cricket is one of the national sports of Guyana and Bourda is the only international cricket ground that is below sea level.
Imports
| Goods | Place of Origin |
|---|---|
| Clothing | Britain |
| Machinery | Britain |
Exports
| Goods | Destination |
|---|---|
| Sugar Cane | Britain |
| Rum | Britain |
| Coffee | Britain |
| Cotton | Britain |
Industry
| Port Industries | Other Industries |
|---|---|
Scarrow Associations
| Scarrow | Period |
|---|---|
| Joseph Scarrow | 1840, 1847, 1856-61 |
| William Scarrow | 1852-53, 1858-59 |
| Robert Scarrow | 1924-27, 1930, 1933, 1938 |








